Al Jazeera: The battle for Area C
Jillian Kestler-DAmours Al Jazeera: 10 Aug 2012
 Palestinians face severe restrictions in the more than 60 per cent of the West Bank under full Israeli control.
Palestinians face severe restrictions in the more than 60 per cent of the West Bank under full Israeli control.
Susya, occupied Palestinian territories – Dozens of tents, made of wooden planks, small boulders and plastic tarps, cling to the rocky hilltop. Tires, garbage, shoes, children’s clothes and broken electronic equipment are strewn between the tents, home to the 400 Palestinian residents of Susya in South Mount Hebron.
“I’m 66 years old. 66 years. I was on this land before Israel [was created]. I was born here,” Mohammad Al-Nawaja’ah, a community leader and elder in Susya, said from inside his family’s tent. “[Israel] is a racist state. They want to take the land from us and give it to the settlers. There is no hope.”
An Israeli settlement, also named Susya, was built in 1983 on a hilltop just across the valley from Palestinian Susya. Today, just beyond an electric gate operated by a gun-wielding Israeli soldier, the settlement has paved roads, two-storey homes, a supermarket, playgrounds and trees lining its streets.
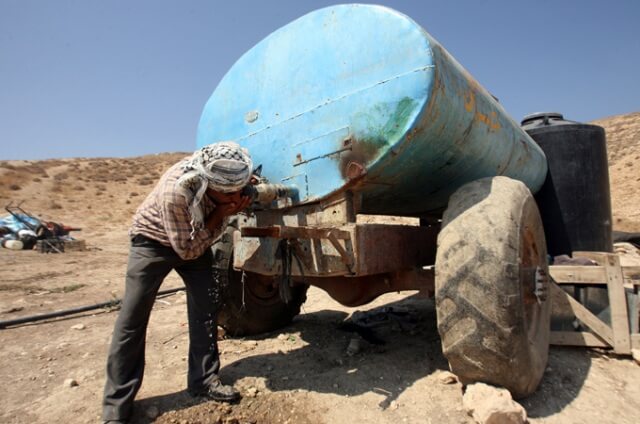
In June, the Israeli Supreme Court issued six immediate demolition orders for Palestinian Susya. The destruction of more than 50 structures – including residential homes, water cisterns and solar energy panels – could happen any day now, and would effectively wipe the entire village off the map.Despite being inhabited since before the creation of Israel, Palestinian Susya isn’t connected either to the electricity or water grids, and lacks school and health facilities. Israel has deemed the village “illegal”.
“If they begin to demolish, we will stay in our land,” Al-Nawaja’ah said. “Where can we go? This is our land.”
Under the Oslo Accords
And Susya isn’t alone. In fact, the village’s fate is similar to nearly all other Palestinian communities located in what is known as “Area C” of the occupied West Bank.
Area C was first delineated in the Declaration of Principles on Interim Self Government Arrangements, otherwise known as the Oslo I agreement, which divided West Bank territory into three separate categories.
Area A is under the control of the Palestinian Authority and encompasses most of the major Palestinian cities. Area B comprises most Palestinian rural communities and is under Palestinian administrative and joint Palestinian-Israeli security control.
Area C is under complete Israeli administrative and military control, and comprises all Israeli settlements – including roads, buffer zones, and other infrastructure – and Israeli military training areas. Less than five per cent of the Palestinian population of the West Bank lives in Area C – yet it covers more than 60 per cent of the Palestinian territory.
In 1995, the Interim Agreement, or Oslo II, was passed. Article 27 of this agreement stipulated that in Area C, “powers and responsibilities related to the sphere of Planning and Zoning will be transferred gradually to Palestinian jurisdiction” by 1999.
But this transfer of powers has yet to be implemented.
Today, some 150,000 Palestinians live in Area C, where they face severe restrictions on planning, building and accessing services and the area’s natural resources. It is estimated that more than 350,000 Jewish-Israeli settlers now also live in Area C, an increase of more than 15,000 in the past year alone, in contravention of international law.
Inequalities in planning and construction
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) reported that 70 per cent of Area C is off-limits to Palestinian construction, while 29 per cent is heavily restricted. The Israeli Civil Administration, the Israeli military body that oversees Area C, has planned less than one per cent of Area C for Palestinian development, OCHA also found.
According to Alon Cohen-Lifshitz, an Israeli architect and director of the Community Planning Department in Area C for Israeli group Bimkom, Planners for Planning Rights, Israeli planning laws make life unbearable for Palestinians in the area.
“The goal is not to allow any development of Palestinians in Area C besides what they must approve. They are creating all the obstacles in planning. Their wish [is] that all the Palestinians which live in Area C will move to Areas A and B,” Cohen-Lifshitz said.
According to the latest official figures obtained by Bimkom, of the 444 building permit applications Palestinians submitted in 2010 in Area C, only four (less than one per cent) were approved. Cohen-Lifshitz also said that only about 15 building plans had been approved for Palestinians in Area C over the past decade.
OCHA reported that in 2011, the Israeli authorities demolished 560 Palestinian-owned structures, including 46 rainwater collection pools, in Area C. That same year, Israel’s demolition policy made more than 1,000 people, more than half of whom were children, homeless.”(Palestinians are) building houses because they don’t have any other opportunities. After they build, they receive a demolition order and after the order, they will try to achieve a building permit. It’s the only chance for them to try to save (their) house or to save time,” he said.
By contrast, Israeli settlements, illegal under international law, are expanding at a rapid pace – and at least 125 settlement outposts, considered illegal even under Israel’s own laws, have been set up on hilltops throughout the West Bank.
“People are living their lives above themselves, for the betterment of the nation of Israel, not just because ‘here’s where I can live’,” said Ariela Deitch, a mother of six and resident of the Israeli outpost of Migron.
Perched on a hilltop overlooking the Palestinian villages of Deir Dibwan and Burqa, just east of Ramallah, 49 Jewish-Israeli families live in a series of 45-square-metre caravan homes in Migron. Set up in the late 1990s, Migron has paved roads, a large water tank, electricity and telecommunication towers, a kindergarten, playgrounds, and a horseback riding child behavioural therapy centre.
But it was illegally built on privately owned Palestinian land and the Israeli government has said it must be evacuated.
Court hearings are ongoing regarding whether 17 families, who say they recently purchased the land legally, can remain in Migron. The rest will be relocated to temporary caravans down the road – a “refugee camp”, according to Deitch – at a reported cost of at least 65m NIS ($16.3m).
“You become very quickly become part of this mountain. It becomes like tearing a tree out by the roots. It’s not going to be simple,” Deitch said. “You feel an importance in that, in that people came up here fair and square. There’s a justice to it.”
A pattern of destruction
In mid-July, the Israeli government announced its intention to forcibly displace ten Palestinian villages in Area C, in the South Mount Hebron area, in order to use the land for military training exercises.
An estimated 3,000 demolition orders remain in place in Palestinian communities of Area C. International agencies are becoming increasingly involved in projects in the area, in what appears to be an attempt to safeguard Palestinians against forced displacement.
This international support drew the ire of the Israeli government in mid-July, when it threatened to withhold work visas and travel documents for employees of the Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the UN agency that works on Palestinian humanitarian projects.
Despite this pressure, Palestinians in Area C are increasingly submitting building plans to the Israeli Civil Administration in an effort to legally develop their towns and villages.
“Master plans could resolve some things; [they] could help in freezing the implementation of these [demolition] orders and could help in the future to legalise the construction inside the adopted and approved Master plans,” said Dr Azzam Hjouj, General Director of the Department of Planning in the Palestinian Authority’s (PA) Ministry of Local Government.
Hjouj explained that while the PA doesn’t have direct authority over Area C, it is currently playing a consultative role and helping local Palestinian councils draft “Master Plans”. To date, almost two dozen Palestinian communities submitted master plans to the Israeli Civil Administration, and another 30 to 40 have expressed a desire to do so.
“The Israelis first, before the Palestinians, said in the final resolution… [that Area C] should return back to the Palestinian Authority,” said Hjouj. “So if the PA looks [to] this area as an integral part of its territory, and wants to help [its] communities in their essential needs – networks, roads, health and education – I think the Israeli party should collaborate in this.”
De facto Israeli annexation
In February, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu established a committee to determine the legality of Israeli settlement outposts in the West Bank. Known as the Levy Committee, it was composed of two Israeli former judges and an Israeli foreign ministry attorney, all major supporters of the settlement project.
The committee concluded that Israel was not an occupying power in the West Bank, that Israeli settlements were legal and that the government should legalise outposts. These findings have led many Israeli, Palestinian and international analysts to conclude that Israel is preparing to annex parts of the West Bank, namely Area C.
“They want to annex more land with less Palestinians and I think Area C gives them this opportunity,” said Shawan Jabarin, Director of Palestinian human rights group Al Haq. “They expanded their jurisdiction over the area by expanding Israeli laws on the settlers in that area, by expanding the authority and the responsibility of the Israeli official and government agencies. It’s de facto annexation.”
According to Mark Regev, spokesperson for the Israeli prime minister’s office, however, allegations that Israel is preparing to annex Area C are “ludicrous”.
“Do you really believe these conspiracy theories that Israel wants to depopulate area C? I mean, it’s rubbish,” Regev told Al Jazeera. “We are prepared to continue peace negotiations with the Palestinians and hopefully sign new agreements. But in the absence of signing new agreements, it’s clear that Israel remains to have jurisdiction in Area C.”
Article 47 of the Fourth Geneva Convention states, however, that the protected population of an occupied territory – in this case, the Palestinians – continue to be protected by the Convention regardless of “any agreement concluded between the authorities of the occupied territories [the Palestinian Authority] and the Occupying Power”.
“Any agreement with the Palestinian side doesn’t give [Israel] the right to annex the area,” Jabarin said. “That’s the main plan: less Palestinians and annex more land.”